Find out how to figure out system safety issues by using various prescribed methods for the purpose.
This course will give you an overview and a classification of methods used to assess the safety of a system. Most common safety analysis methods are laid out and their workflows are described in detail. The course has a high practical dimension, with numerous examples including group work for course participants, which will conduct each method over a practical technical system of choice. The practical exercises would focus on the automotive domain, with analysis tackling specifics of hardware and software components in a system safety decomposition.
Course topics:
- Introduction to safety analysis methods, system model analysis
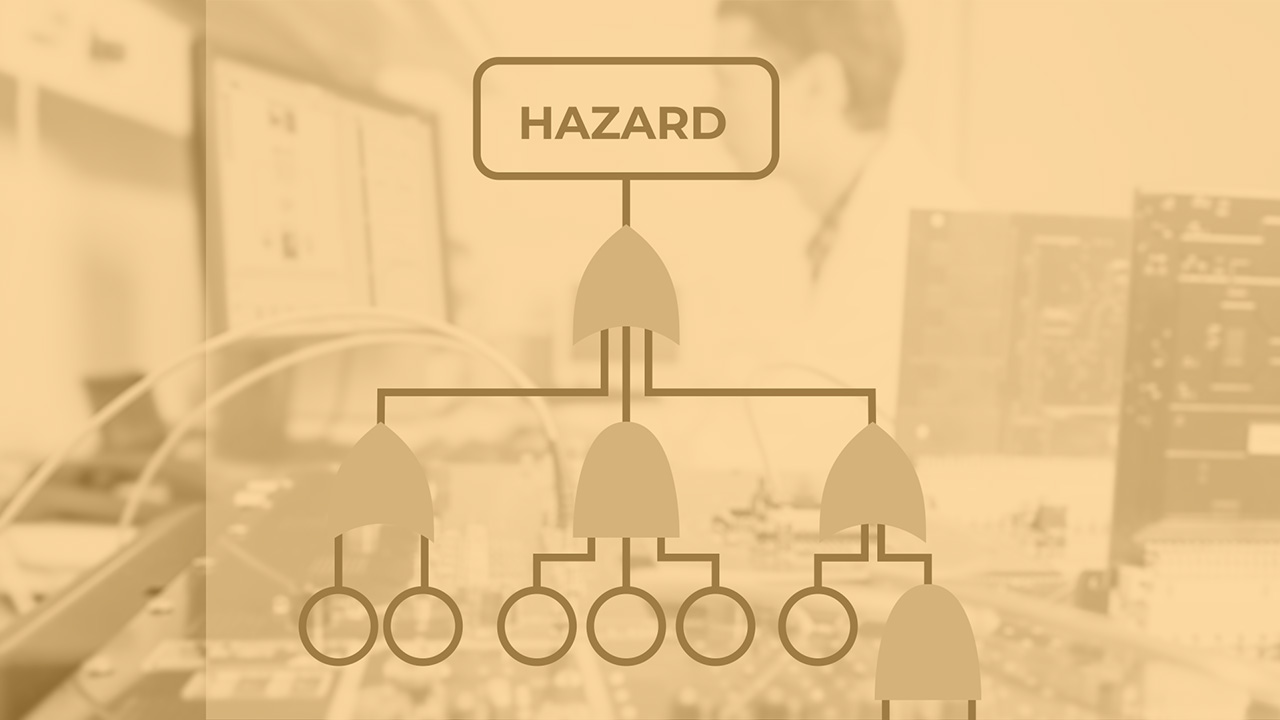
- Preliminary Hazard List (PHL), Preliminary Hazard Analysis (PHA), Failure Mode and Effect Analysis variants (FMEA/FMEDA/FMECA/Fu-FMEA), Functional Failure Analysis (FFA), Hazard and Operability Analysis (HAZOP), Fault Tree Analysis (FTA), Event Tree Analysis (ETA), Dependent Failure Analysis (DFA)
- New analysis in the context of ISO 21448 SOTIF, such as System-Theoretic Process Analysis (STPA)
- Key quantification (such as Safe Failure Fraction and Diagnostic Coverage)
- Hazard identifications, minimal cut sets, assessment of dependent failures and potential weaknesses
- Identification and analysis of common cause failures, Identification, and analysis of cascading failure, Assessment of their risk of violating a safety goal
- Mitigation: definition of safety measures
Modules:
M1: Introduction to safety analysis methods
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/SAT-M1.png
This lecture will cover a general definition of safety analysis methods, their categorization, and an overview of their limitations.
Creating a list of requirements for your system.
2 hours 30 minutes
M2: System model analysis
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/SAT-M2.png
This lecture will include a quick recap of the system, a guide to model build-up, and examples.
Analyzing your ECU and building a system view.
2 hours 30 minutes
M3: Hazard and Operability Analysis (HAZOP) and Functional Failure Analysis (FFA)
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/SAT-M3.png
This lecture will focus on conducting a Hazard and Operability Analysis (HAZOP) and Functional Failure Analysis (FFA), with an emphasis on hazard and operability study.
Applying eFFA, investigating root causes and effects, identifying consequences, defining operation modes, and analyzing permutations.
2 hours 30 minutes
Project 1
none
none
Participants are required to apply the concepts from exercises in their group assignments.
8 hours
M4: Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/SAT-M4.png
This lecture will cover the basics of Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), its various types, moderation techniques, and discuss its advantages, disadvantages, and hints.
Conducting an FMECA analysis, evaluating failure modes, detection possibilities, RPN, and countermeasures.
2 hours 30 minutes
M5: Fault Tree Analysis
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/SAT-M5.png
This lecture will introduce the basics of Fault Tree Analysis (FTA), hazard identification, minimal cut sets, systematic fault tree construction, and special applications such as success trees and tolerability calculations.
Creating a common hazard list from eFFA and FMECA, and analyzing the hazards using FTA.
2 hours 30 minutes
Project 2
none
none
Participants are required to apply the concepts from exercises in their group assignments.
8 hours
M6: Hazard analysis – PHL and PHA
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/SAT-M6.png
This lecture will provide an introduction to hazard analysis, focusing on the Preliminary Hazard List (PHL) and Preliminary Hazard Analysis (PHA).
Developing a rough concept and PHL (Preliminary Hazard List) for your system and preparing a separate PHA (Preliminary Hazard Analysis).
2 hours 30 minutes
M7: System-Theoretic Process Analysis (STPA)
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/SAT-M7.png
This lecture will delve into System-Theoretic Process Analysis (STPA), covering Systems Theory, the STAMP model, defining purpose, identifying system-level hazards and constraints, modeling the control structure, identifying Unsafe Control Actions (UCA), defining controller constraints, and identifying loss scenarios that lead to Unsafe Control Actions, Identifying scenarios in which control actions are improperly executed or not executed.
Applying STPA hazard analysis to your SCS.
2 hours 30 minutes
Project 3
none
none
Participants are required to apply the concepts from exercises in their group assignments.
8 hours
M8: Dependent Failure Analysis (DFA)
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/SAT-M8.png
This lecture will focus on Dependent Failure Analysis (DFA), including the assessment of dependent failures in integrated circuits, identification and analysis of common cause and cascading failures, evaluation of their risk in violating safety goals, and the definition of mitigation safety measures.
none
2 hours
Final exam
none
none
none
1 hour 30 minutes
Requirements
Hardware: Computer with Internet connection, working speakers and microphone.
Software: Chrome browser.
Prior knowledge: Students should have basic engineering knowledge in either one of the following disciplines: electrical engineering, computer engineering, or mechanical engineering.