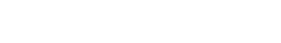Master the Art of Automotive Safety with ISO/PAS 21448 (SOTIF).
This course provides an in-depth study of safety principles, standards, and practices essential for modern automotive systems, with a primary focus on ISO 21448 (SOTIF). It begins by exploring the definitions of safety, contrasting it with security, and examining key concepts such as hazards, risks, and the causal chain of failures. Participants will gain insight into safety standards, including ISO 21448, ISO 26262, ISO 8800, ISO 5083, and UL4600, as well as their evolution and application in autonomous systems. Modules cover the specification and design of intended functionality, operational design domain (ODD), and requirements engineering, offering practical tools for eliciting, documenting, and managing safety requirements. The course emphasizes hands-on learning through System Theoretic Process Analysis (STPA) to identify hazards, unsafe control actions, and loss scenarios, including triggering conditions and human factors with misuse cases. Students will also learn about risk evaluation, acceptance criteria, and validation strategies to ensure safety targets are met. The course culminates with constructing a compelling safety case using techniques like Goal Structuring Notation (GSN) and insights from the UL4600 standard for autonomous vehicle safety.
Course Topics:
- Explore safety concepts, hazards, risks, and the causal chain of failures
- Understand ISO 21448, ISO 26262, ISO 8800, ISO 5083, UL4600, and their integration in automotive systems
- Learn the terminology, management, and work products of the SOTIF standard
- Define functionality, performance targets, dependencies, and warning strategies
- Perform hazard identification, unsafe control actions analysis, and loss scenario mapping
- Develop risk acceptance criteria and validation strategies for autonomous systems
- Construct and present safety cases using Goal Structuring Notation (GSN) and UL4600 guidelines
Modules:
M1: General safety (systems, functional, intended)
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/FSS-M1.png
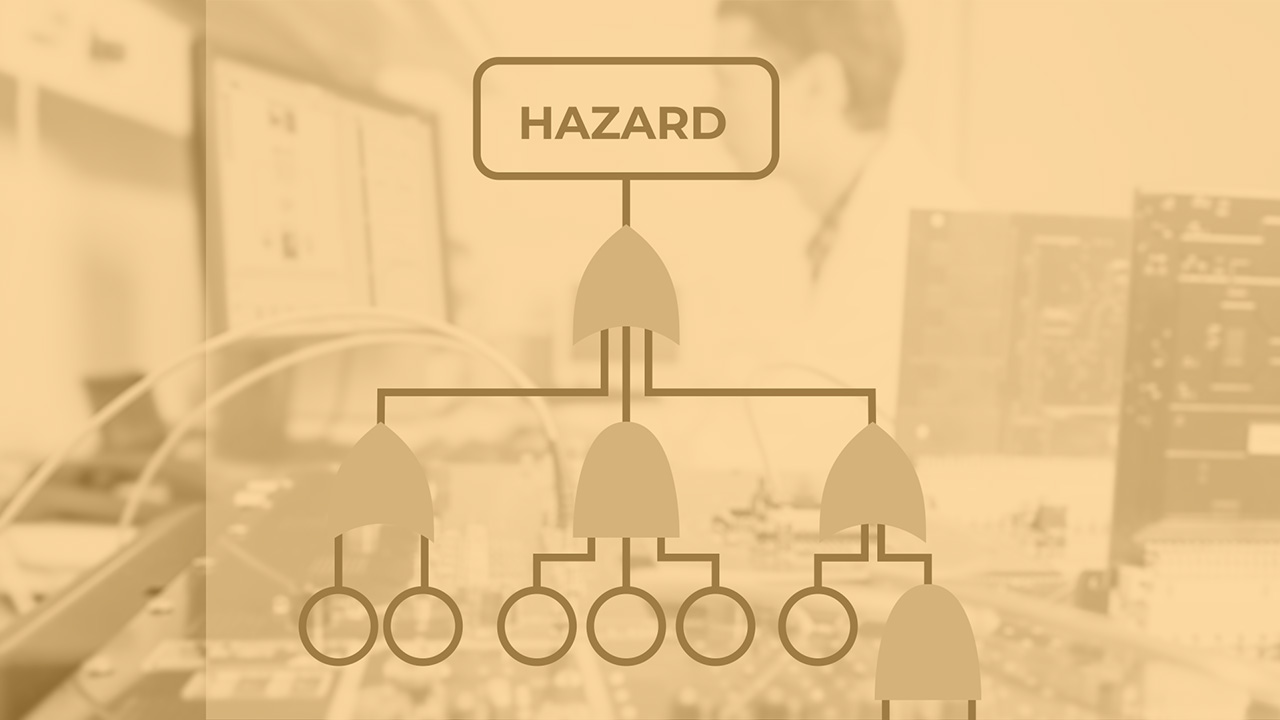
Understanding the definition of safety and its nuances in different application domains, and differences compared to security. The lecture examines various parts of the safety iceberg: from the accidents and incidents, up to their underlying pathology – a causal chain of faults, errors, and failures, and on the other side, the manifestations – hazards and risks with accompanying methods to measure and quantify them.
Additional aspects specific to SOTIF risks are introduced: foreseeable misuse and functional insufficiencies (specification and performance).
Furthermore, learning the similarities and differences between system and functional safety, together with the definition of the necessary aspects like the safe state, the safety function, and the safety integrity. The lecture provides an overview of the rich canvas of available technical standards and motivates the necessity and importance of standards.
none
1 hour 30 minutes
M2: Safety Standards – canvas, scope, interactions
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/sotif_2.png
Laying out some basic details of the key technical safety standards – from generic umbrella standard IEC 61508 for primarily one-off systems (e.g. plants), up to the most relevant automotive safety standards (both FuSa and SOTIF, but also safety of the AI and ways how to construct a safety case for the ADS).The lecture provides details about the standards, their genesis, motivation, as well as, key building blocks and ideas that were followed when creating the automotive standard for road vehicles (ISO 2626 and ISO 21448). Finally, the lecture contrasts the differences but also complementary nature of the two automotive standards – how to go beyond the legacy automotive E/E systems towards building the autonomous driving systems.
none
2 hours
M3: ISO 21448 – Overview, Terminology, Management, and Work Products
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/sotif_3.png
Introducing the contents, structure, workflow, life-cycle of the standard with appropriate methods to read it and understand the necessary terms from the vocabulary (both ISO 21448 and ISO 22736 – SAE J3016). The lecture further dwells on the SOTIF principles, including related hazardous event model and four scenario areas ((not)hazard/(not)known) to derive goals – perform a risk acceptance evaluation and reduce the probability of hazardous scenarios either through functional modification and/or adequate verification and validation strategy.
none
2 hours
M4: ISO 21448 – Intended functionality (IF) – specification and architectural design considerations
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/sotif_4.png
Learning how to correctly describe and understand the intended functionality (ODD, authority, strategy, …), corresponding performance targets for enabling peripherals (sensor/controller/actuator), dependencies, interactions or interfaces of the IF (driver, road users and infrastructure, communication exchange, etc.).
Finally, how to describe a warning and degradation concept (warning strategies, DDT takeover/fallback conditions and schemes, etc.) and procedures supporting data collection and monitoring (during and after development of the intended functionality).
none
2 hours
M5a: ISO 21448 – STPA – overview and step 1 – purpose (loss and hazards)
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/sotif_5a.png
The focus of the lecture is to provide practical (hands-on) knowledge on how to perform SOTIF hazard identification in practice.
Students will get a chance to learn to execute STPA (System Theoretic Process Analysis).
Motivation for introduction of the STPA, as well as step 1 of the analysis are covered in details. Focus is to lay the foundation for the consecutive steps by reusing and reframing the work done while describing the intended functionality. Finally, students will get a chance to define key terms like loss, hazards, and system constraints for their intended functionality of choice.
none
2 hours
M5b: ISO 21448 – STPA – steps 2 and 3 – unsafe control actions w/ misuse
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/sotif_5b.png
The aim of the lecture is to illustrate how the 2nd and 3rd step of the STPA are properly executed and how their results help to complete the requirements from the Chapters 6 and 7 of SOTIF standard. Students will learn how to “Model the Control Structure” (step 2) with a single goal: to model the internal representation of our system. We start by recognizing the control building blocks and then describe the interactions among them: control actions and feedback.
Finally, the lecture provides further practical (hands-on) knowledge on how to identify and describe unsafe control actions stemming from the interaction of the driver/user with the system including reasonably foreseeable misuse (direct or indirect).
none
2 hours
M5c: ISO 21448 – STPA – step 4 – loss scenarios + HF
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/sotif_5c.png
Continuing further with concluding aspects of the STPA in practice – determining the loss scenarios. This is where things get interesting. STPA looks for the causal factors that can lead to the unsafe control actions and to hazards. For example, a bright sun glare could interfere with the car’s camera, causing it to misjudge the proximity of a nearby vehicle. Furthermore, the vehicle can have the inconsistent process model e.g., believing that there are no obstacles due to incorrect or missing information from the sensors. Loss scenario step helps us determine where UCAs might emerge within the system control flows.
Finally, the lecture provides guidance on how to encounter for human factor i.e. how to identify the reasonably foreseeable misuse (direct and indirect) and triggering conditions.
none
1 hour
M6: ISO 21448 – STPA loss scenarios + risk evaluation, acceptance criteria, and validation targets
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/sotif_6.png
The lecture provides insights on how to understand, evaluate, determine, and assign appropriate risk parameters (severity, controllability, exposure, and occurrence).
Once the foundation is set, the lecture showcases main difference between FuSa and SOTIF when evaluating whether risk is unreasonable.
Appropriate risk acceptance criteria is defined, illustrated, and a systematic way how to structure the selection is presented.
Furthermore, the lecture discusses acceptance criteria for the residual risk considering governmental and industry regulations, maturity of the function on the market, nominal driver performance, available traffic data etc.
Finally, validation target concept is put in context of area 2 and 3 scenarios and practical ways how to calculate it are laid out.
none
2 hours
M7: Verification and Validation
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/sotif_7.png
The lectures focus on the right side of the proverbial V-model, where the idea is to provide a strategy that will yield evidence that the SOTIF-related vehicle-level residual risk is below an acceptable level and elements meet their functional requirements and the coverage over the operational design domain (ODD) is sufficient.
The students will get familiar with both evaluation of the known and unknown hazardous scenarios and learn about various testing methods, their goals, necessary steps and how to translate them into real projects.
none
2 hours
M8: Safety Case
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/sotif_12.png
To conclude the lectures, the students have the opportunity to learn about the seminal work product answering the fundamental question “How do we know that our system is safe enough?”.
The lecture explores several possible approaches to construct a safety case, to provide appealing arguments, and to be able to convince the safety assessors (like a jury in the court case).
Students will learn about the simple textual form, structured prose (XML-alike format), and a graphical way (Goal Structuring Notation (GSN)[currently being standardized and widely used.])
The latest development in formulating and structuring the safety case for autonomous vehicles (UL4600 standard) is explained with key concepts (structure of the standard, prompts and their rigor, and most importantly Safety Performance Indicators).
none
12 hours
Final exam
none
none
none
1 hour 30 minutes
Requirements
Software: Chrome browser.
Hardware: Computer with an Internet connection, working speakers, and microphone.
Prior knowledge: Students should have basic engineering knowledge in either one of the following disciplines: electrical engineering, computer engineering, or mechanical engineering.