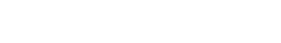M1: General safety
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/FSS-M1.png
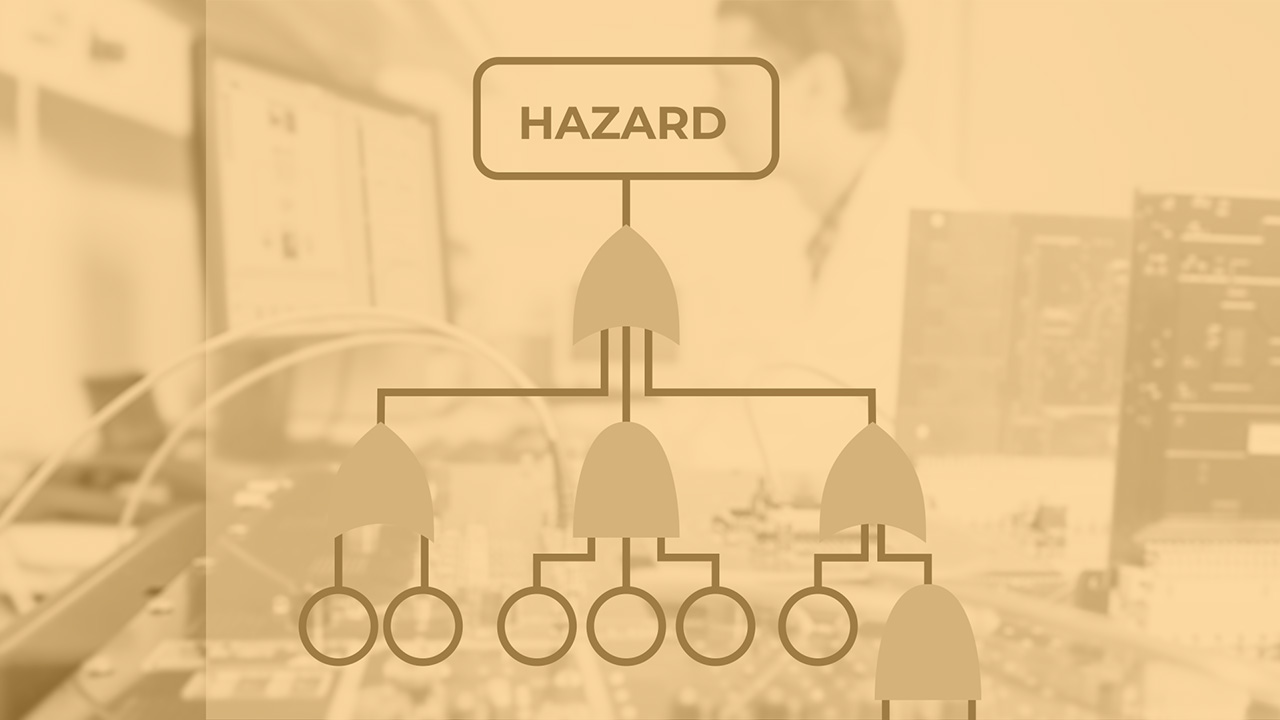
Understanding the definition of safety and its nuances in different application domains, and differences compared to security. The lecture examines various parts of the safety iceberg: from the accidents and incidents, up to their underlying pathologies – a causal chain of faults, errors, and failures, and on the other side, the manifestations – hazards and risks with accompanying methods to measure and quantify them.
Analyzing a system, identifying fault-error-failure chains, assessing risks and hazards, proposing mitigation measures, and discussing Common Cause Failures.
1 hour 30 minutes
M2: System and Functional Safety
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/FSS-M2.png
Learning the similarities and differences between system and functional safety, together with the definition of the necessary aspects like the safe state, the safety function, and the safety integrity. The lecture provides an overview of the rich canvas of available technical standards and motivates the necessity and importance of standards.
Identifying and documenting hazards and corresponding risks, proposing risk mitigation measures.
2 hours
M3: Safety Standards
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/FSS-M3.png
Laying out some basic details of the key technical safety standards – from generic umbrella standard IEC 61508 for primarily one-off systems (e.g. plants), through machinery standards IEC 62061 and ISO 13849 for systems produced in smaller batches (e.g. production machines), up to the most relevant automotive safety standard ISO 26262 focusing on cars manufactured in masses. The lecture provides details about the standards, their genesis, motivation, as well as, key building blocks and ideas that were followed when creating the automotive standard for road vehicles (ISO 2626). Finally, the lecture sheds some light on the novel complementary automotive standard focusing on the safety of the intended functionality (SOTIF – ISO/PAS 21448), essential when building the autonomous driving features.
Describing a ADAS feature, identify and document issues across various categories, and proposing testing scenarios addressing each identified issue.
2 hours
M4: ISO 26262 – Overview, Management, and Work Products
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/FSS-M4.png
Introducing the contents, structure, workflow, life-cycle of the standard with appropriate methods to read it and understand the necessary terms from the vocabulary. The lecture further dwells on the management structure, culture, goals, and roles to execute the entire safety process. Required documents (work products) as output from the process are introduced, classified, and visualized by highlighting the interactions. Moreover, the lecture concludes on mandated confirmation measures that guarantee the correctness and completeness of the content of work products.
Analyzing safety anomalies are handled, classifying work products, and reviewing project documents.
2 hours
M5: ISO 26262 – Concept Phase – HARA
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/FSS-M5.png
Learning how to correctly define items (functionalities at vehicle level perceivable to the driver) and perform hazard analysis and risk assessment (HARA) in practice. The focus of the lecture is on the early HARA stages – team formation, the definition of the Operating Modes (OpMods), and determining relevant functional faults using Hazard and Operability Study (HAZOP). Students will get a chance to learn how to identify the most representative scenarios (operating situations – OpSits) where the item faults could potentially exhibit hazards.
Analyzing a vehicle functionality with defined operating modes and requirements, create a functional block diagram, and applying HAZOP, and defining operating scenarios.
2 hours
M6: ISO 26262 – Concept Phase – ASIL
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/FSS-M6.png
Continuing further with concluding aspects of the HARA in practice – determining the automotive safety integrity level (ASIL) by creating the risk assessment matrix (combination of OpMod failures and OpSits) and evaluating and assigning appropriate risk parameters. The lecture provides insights on how each of risk parameters (severity, controllability, and exposure) is determined, and how it contributes to the conclusive ASIL rating. Finally, the lecture concludes by introducing the top-level safety requirements (safety goals) and their characteristics (safe state and fault tolerance time (FTT)) and properties (warning and degradation concept), as a foundation for consecutive safety development.
Combining relevant failures and operational situations (OpSits) in a Risk Matrix, assigning severity, controllability, and exposure levels, determine the highest ASIL for OpMod faults, and formulating top-level safety goals with necessary characteristics and properties.
2 hours
Project 1
none
none
Completing the Hazard Analysis and Risk Assessment (HARA) for your selected item, determine the ASIL, and describe the safety goals by revising and extending the results from exercises, ensuring accuracy and thoroughness to reflect a real-world scenario.
10 hours
M7: ISO 26262 – ASIL and safety-oriented analysis
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/FSS-M7.png
Safety goals provide a starting point for the rest of the development on a system, hardware, and software level and can be assigned to one or several elements. Harmonious and safe operation of the overall system can be provided if composing elements coexist without negatively influencing each other. The lecture provides insights on how a composite system is implemented with elements of different ASIL.
Furthermore, the lecture examines how the established ASIL for a requirement could be reduced and mapped to redundant ones by using the ASIL decomposition.
Evaluating ASIL decomposition methods in ISO 26262, and impact to ASIL levels and requirements.
2 hours
M8: ISO 26262 – Functional and Technical Safety Concepts
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/FSS-M8.png
The lecture explores how the safety goals should trickle down and create further child requirements on functional and system-level – a foundation of the system architecture and appropriate safety measures. Applied requirement engineering should focus on several aspects like detection and control of faults in the element itself and other elements, measures to reach or keep them safe state, measures to implement the warning and degradation concept, and finally on measures and test interval requirements to avoid latent faults.
Developing Functional and Technical Safety Concepts for a specific safety goal, including Functional Safety Requirements (FSRs) and Technical Safety Requirements (TSRs).
2 hours
M9: ISO 26262 – Verification and Validation
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/FSS-M9.png
The lecture focuses on the right side V-model, where the idea is to make sure that we have correctly implemented all the required functionalities. Integration and Test Strategy lays out the necessary steps on several abstraction levels (hardware-to-software, system, and, vehicle) with an appropriate timeline and corresponding testing report to provide evidence. The students will get familiar with and learn about various testing methods focusing on requirements, safety mechanisms, interfaces, diagnostic coverage, and robustness.
Proposing a testing plans for, and providing justification and a general overview of expected testing activities.
2 hours
M10: ISO 26262 – Software Development
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/FSS-M10.png
Discussion about the prevalence of software in modern car items (especially autonomous driving), highlights the corresponding safety impact and prudence that one has to apply when developing the software. Practical examples give hands-on guidance about the necessary methods required by the standard when designing, developing, and implementing software architecture and units.
Analyzing software architecture, design documents, and source code, evaluate their compliance with ISO 26262 requirements, identify gaps, and propose corrective actions based on the standard’s tables.
2 hours
M11: ISO 26262 – Software Verification
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/FSS-M11.png
Corresponding methods from the right side of the V-model are examined – how to verify software architecture, how to devise software unit level tests, and demonstrate adequate structural coverage. Additional details, like software tool qualification and confidence level, are examined.
The lecture concludes by visiting some of the more obscure and less documented parts of the ISO 26262 standard, like safety elements out of context (SEooC), proven in use elements, and configurable software.
Establish Tool Confidence Level (TCL), and draft a qualification description covering various aspects like malfunction detection, expected behavior under anomalies, and usage constraints.
2 hours
M12: ISO 26262 – Safety Case
https://academy.nit-institute.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/FSS-M12.png
To conclude the lectures, the students have the opportunity to learn about the seminal work product answering the fundamental question “How do we know that an item is safe enough?”.
The lecture explores several possible approaches to construct a safety case, to provide appealing arguments, and to be able to convince the safety assessors (like a jury in the court case). Students will learn about the simple textual form, structured prose (XML-alike format), and a graphical way (Goal Structuring Notation (GSN)[currently being standardized and widely used.])
Analyzing a safety case document, and evaluating the safety case if it uses GSN.
2 hours
Project 2
none
none
Completing the Functional and Technical Safety Concepts, developing software requirements, creating a Testing Plan, and devising Test Cases across different integration levels, ensuring accuracy and alignment with previously established Safety Goals.
10 hours
Final exam
none
none
none
1 hour 30 minutes